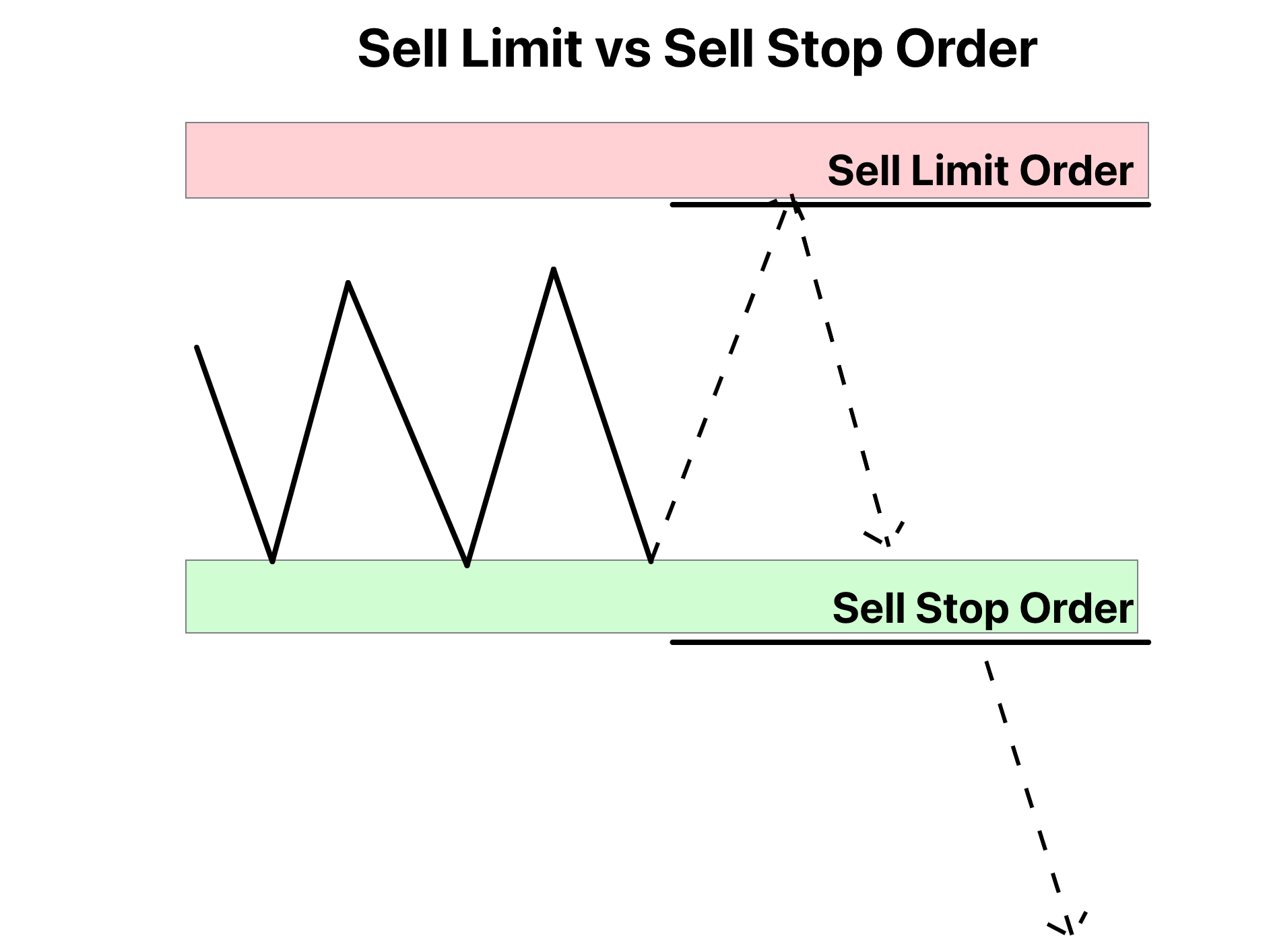
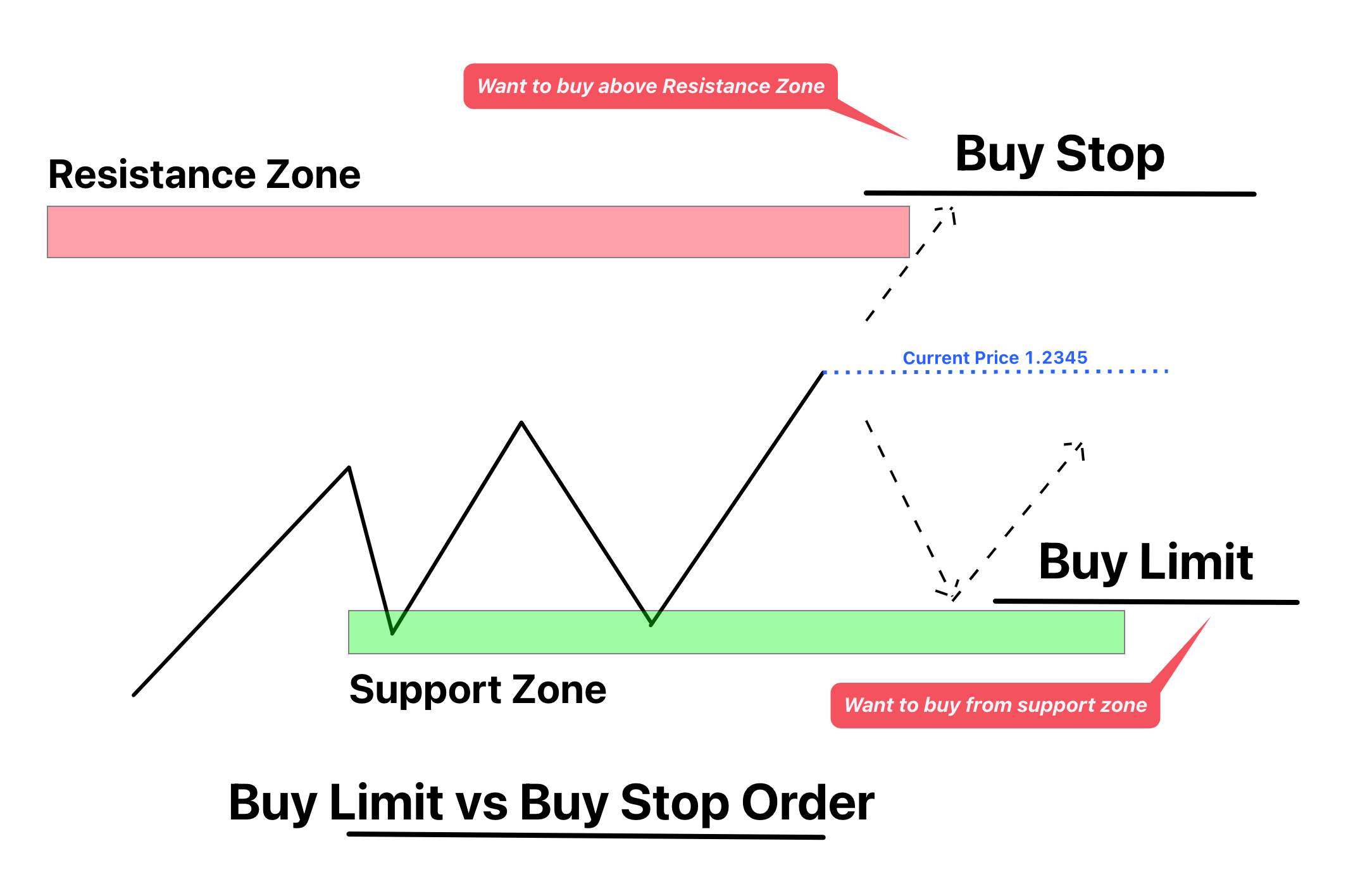
They combine the features of stop orders and limit orders, allowing investors to set specific conditions for buying or selling securities. This dual-layered approach provides a safety net against unexpected price movements while ensuring that trades are executed only at desired price levels. Understanding how stop limit orders work is crucial for anyone seeking to enhance their trading strategy and protect their investments in today's fast-paced financial landscape. The concept of stop limit orders has become increasingly relevant in modern trading environments where market fluctuations can happen in milliseconds. These orders serve as a bridge between traditional market orders and more sophisticated trading mechanisms, offering traders greater control over their transactions. By setting both a stop price and a limit price, investors can create a buffer zone that helps prevent significant losses during market turbulence. This mechanism has proven particularly valuable in electronic trading platforms where algorithmic trading dominates the landscape. As we delve deeper into the world of stop limit orders, it's important to recognize their role in modern portfolio management. These orders aren't just tools for individual traders; institutional investors and professional money managers frequently incorporate them into their trading strategies. The flexibility they offer in terms of price protection and execution certainty makes them an essential component of contemporary trading practices. Whether you're a seasoned investor or just beginning your financial journey, understanding stop limit orders can significantly enhance your ability to navigate complex market conditions.
Table of Contents
- What Are Stop Limit Orders and How Do They Work?
- Why Should You Use Stop Limit Orders in Your Trading Strategy?
- How to Set Up an Effective Stop Limit Order?
- What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Stop Limit Orders?
- Stop Limit Order vs. Stop Loss Order: What's the Difference?
- Advanced Techniques for Using Stop Limit Orders in Volatile Markets
- Real-World Examples of Successful Stop Limit Order Implementation
- What Does the Future Hold for Stop Limit Order Technology?
What Are Stop Limit Orders and How Do They Work?
A stop limit order combines two essential components: the stop price and the limit price. The stop price acts as a trigger point that activates the order when reached, while the limit price sets the maximum or minimum price at which you're willing to execute the trade. This dual mechanism creates a safety net for traders, ensuring that their orders are only filled within a specified price range. When the market price reaches the stop price, the order converts into a limit order, which will only execute at the limit price or better.
The functionality of stop limit orders becomes particularly valuable in fast-moving markets. For instance, if you own shares of a technology company currently trading at $50, you might set a stop price at $45 and a limit price at $44. This setup means that if the stock price falls to $45, your order becomes active, but it will only execute if the price remains above $44. This approach helps prevent situations where rapid price declines could result in execution at significantly lower prices than anticipated.
Read also:Explore The World Of 300 Hdmovies4u A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding the sequence of events in stop limit order execution is crucial for effective implementation. First, the market price must reach the predetermined stop price. Once this trigger point is hit, the order transitions into a limit order. The trading system then attempts to fill the order at the specified limit price or better. This process typically occurs within milliseconds in electronic trading platforms, though various factors such as market liquidity and trading volume can influence the actual execution time and success of the order.
Why Should You Use Stop Limit Orders in Your Trading Strategy?
Stop limit orders offer several distinct advantages that make them indispensable in modern trading strategies. First and foremost, they provide precise control over trade execution prices. Unlike market orders that execute immediately at current market prices, stop limit orders ensure that your trades only occur within your specified price parameters. This control is particularly valuable in volatile markets where prices can swing dramatically in short periods.
Another significant benefit is the enhanced risk management capability they offer. By setting both a stop price and a limit price, traders create a defined risk-reward framework for each trade. This dual-layer protection helps prevent substantial losses while still allowing for potential gains. For example, a trader might use stop limit orders to protect profits on winning positions while maintaining flexibility for further upside potential. The ability to automate this risk management process reduces emotional decision-making during market turbulence.
Moreover, stop limit orders contribute to better capital efficiency and portfolio management. They allow traders to maintain positions while setting clear boundaries for acceptable price movements. This approach enables more efficient use of trading capital and helps maintain portfolio balance. The flexibility of stop limit orders also supports various trading styles, from day trading to long-term investing, making them suitable for different market participants and investment objectives.
How to Set Up an Effective Stop Limit Order?
Step-by-Step Guide to Placing a Stop Limit Order
Setting up a stop limit order requires careful consideration and precise execution. Begin by analyzing the security's price action and identifying key support and resistance levels. For a sell stop limit order, set the stop price slightly below the current market price, typically at a level where you believe the price momentum might accelerate downward. The limit price should be placed below the stop price, creating a buffer zone that accounts for potential price slippage during execution.
When placing a buy stop limit order, the process works in reverse. Set the stop price above the current market price, usually near a breakout level or resistance point. The limit price should be positioned above the stop price, allowing for price fluctuations during the order execution phase. Most trading platforms provide intuitive interfaces for setting these parameters, often with visual representations of price levels on charts.
Read also:Rainbow Kiss Viral Video The Story Behind The Sensation
Consider these crucial factors when configuring your stop limit order:
- Market volatility and average daily price range
- Liquidity of the security being traded
- Time of day and potential news events affecting the market
- Historical price patterns and support/resistance levels
- Your overall risk tolerance and position size
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using Stop Limit Orders
One frequent error traders make is setting the stop price too close to the current market price, which can lead to premature order activation. This mistake often occurs when traders fail to account for normal price fluctuations and market noise. Another common pitfall is placing the limit price too far from the stop price, potentially resulting in missed execution opportunities during rapid price movements.
Traders sometimes overlook the importance of adjusting stop limit orders as market conditions change. Failing to update these orders can lead to outdated parameters that no longer reflect current market dynamics or your trading objectives. Additionally, many investors make the mistake of using the same stop limit parameters across different securities without considering each asset's unique volatility characteristics and trading patterns.
To optimize your stop limit order strategy, regularly review and adjust your parameters based on:
- Recent price action and volatility metrics
- Changes in market conditions and trading volume
- Upcoming earnings reports or economic events
- Technical analysis indicators and patterns
- Your evolving risk management requirements
What Are the Key Advantages and Disadvantages of Stop Limit Orders?
While stop limit orders offer significant benefits, they also come with notable drawbacks that traders must carefully consider. One primary advantage is the precise price control they provide, allowing traders to define exact entry and exit points for their positions. This feature helps maintain discipline in trading strategies and prevents emotional decision-making during volatile market conditions. Additionally, stop limit orders enable traders to automate their risk management process, freeing up time for other market analysis activities.
However, several disadvantages warrant careful consideration. The most significant drawback is the possibility of partial fills or complete order cancellation if the market moves too quickly through the specified price range. During periods of extreme volatility, the market price might jump directly from above the stop price to below the limit price, leaving the order unfilled. This situation can be particularly problematic in fast-moving markets or during after-hours trading sessions.
Another limitation is the complexity involved in setting appropriate parameters. Determining optimal stop and limit prices requires thorough market analysis and understanding of price action. Traders must balance the need for price protection with the risk of missing out on favorable trades. Moreover, the dual-price structure can sometimes lead to confusion, especially for novice traders who might mistake stop limit orders for simpler stop loss orders. The potential for order expiration without execution also exists, particularly when using day orders that don't carry over to the next trading session.
Stop Limit Order vs. Stop Loss Order: What's the Difference?
Key Differences Between Stop Limit and Stop Loss Orders
While both stop limit orders and stop loss orders serve as risk management tools, they operate fundamentally differently in execution. A stop loss order converts into a market order once the stop price is triggered, ensuring execution but not guaranteeing the price. In contrast, a stop limit order becomes a limit order upon activation, providing price protection but not execution certainty. This distinction becomes particularly crucial during periods of high market volatility when price gaps can occur between the stop price and execution price.
The execution mechanism of these orders reveals another significant difference. Stop loss orders prioritize trade execution, meaning they will fill at the best available market price once triggered, regardless of how far the price might have moved. This approach ensures that positions are closed or opened as intended, but it can lead to substantial price slippage. Stop limit orders, on the other hand, prioritize price protection by setting a maximum or minimum execution price, but this can result in partial fills or no execution at all if the market moves rapidly through the specified price range.
Market conditions significantly influence the effectiveness of each order type. During normal trading conditions with adequate liquidity, both orders function effectively. However, in fast-moving markets or during news events, stop loss orders tend to provide more reliable execution, while stop limit orders offer better price protection. The choice between these order types often depends on the trader's risk tolerance and specific trading objectives.
When Should You Choose a Stop Limit Order Over Other Options?
Several scenarios make stop limit orders particularly advantageous. When trading in markets with sufficient liquidity and moderate volatility, stop limit orders provide excellent price control while maintaining reasonable execution probability. They're especially useful for traders who prioritize avoiding unfavorable prices over ensuring immediate execution. For instance, when trading large-cap stocks with tight bid-ask spreads, stop limit orders can help secure better execution prices while minimizing slippage risks.
The decision to use stop limit orders should also consider specific trading circumstances:
- When maintaining precise control over execution prices is crucial
- During regular trading hours when market depth is sufficient
- When trading securities with predictable price patterns
- For managing positions in less volatile market conditions
- When partial fills are acceptable compared to unfavorable prices
Conversely, stop loss orders might be preferable during earnings announcements, economic data releases, or other events that could cause significant price gaps. They're also more suitable for highly volatile securities or during after-hours trading when liquidity might be limited. Traders should carefully evaluate their risk management needs, market conditions, and trading objectives when deciding between these order types.
Advanced Techniques for Using Stop Limit Orders in Volatile Markets
Experienced traders employ sophisticated strategies to maximize the effectiveness of stop limit orders in volatile market conditions. One advanced technique involves using multiple stop limit orders at different price levels, creating a layered protection system. This approach allows traders to manage risk more granularly while maintaining flexibility in their trading positions. For instance, a trader might set a primary stop limit order at a conservative level while placing additional orders at more aggressive levels to capture different market scenarios.
Another sophisticated method involves combining stop limit orders with other order types and trading tools. Traders often integrate stop limit orders with trailing stops, which automatically adjust the stop price as the market moves favorably. This combination provides dynamic risk management while maintaining price protection. Additionally, using conditional orders that trigger stop limit orders based on specific technical indicators or price patterns can enhance execution timing and accuracy.
During periods of heightened volatility, traders