Understanding Pritchard Colon is essential for anyone experiencing gastrointestinal issues or seeking clarity about this rare condition. Pritchard Colon, also known as colonic inertia, is a medical condition that affects the large intestine's ability to contract properly, leading to chronic constipation and other digestive problems. This condition is often misunderstood, and its symptoms can overlap with other gastrointestinal disorders, making accurate diagnosis and treatment challenging. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for Pritchard Colon, providing you with the information you need to navigate this condition effectively.
Pritchard Colon is not just a minor inconvenience; it can significantly impact your quality of life. Chronic constipation, bloating, and abdominal pain are common symptoms that can disrupt daily activities and lead to emotional distress. Many individuals with this condition may feel isolated or frustrated due to the lack of awareness and understanding surrounding it. However, with the right knowledge and medical guidance, managing Pritchard Colon is possible.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of Pritchard Colon, offering insights into its causes, symptoms, and diagnostic procedures. We will also discuss treatment options, lifestyle changes, and expert advice to help you take control of your health. Whether you are newly diagnosed or seeking additional information, this guide is designed to empower you with the tools you need to make informed decisions about your well-being.
Read also:Does Meacutelanie Joly Have A Daughter Exploring The Life And Family Of Canadas Prominent Politician
Table of Contents
- What is Pritchard Colon?
- Common Symptoms of Pritchard Colon
- The Diagnosis Process
- Causes and Risk Factors
- Treatment Options for Pritchard Colon
- Lifestyle Changes to Manage Symptoms
- Dietary Recommendations
- Medical Interventions and Procedures
- The Emotional Impact of Pritchard Colon
- Conclusion and Next Steps
What is Pritchard Colon?
Pritchard Colon, or colonic inertia, is a condition characterized by the large intestine's inability to move stool effectively through the colon. This results in chronic constipation, which can be both physically and emotionally taxing. Unlike typical constipation, which may be resolved with dietary changes or over-the-counter medications, Pritchard Colon is a chronic condition that often requires specialized medical attention.
The colon, or large intestine, plays a crucial role in the digestive process by absorbing water and forming stool. In individuals with Pritchard Colon, the muscles of the colon fail to contract properly, leading to a slowdown in the movement of stool. This can cause a buildup of waste in the colon, resulting in symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and infrequent bowel movements.
While the exact cause of Pritchard Colon is not fully understood, researchers believe it may be linked to abnormalities in the nerves or muscles of the colon. Some cases may also be associated with underlying medical conditions, such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or pelvic floor dysfunction. Understanding the underlying mechanisms of this condition is essential for developing effective treatment strategies.
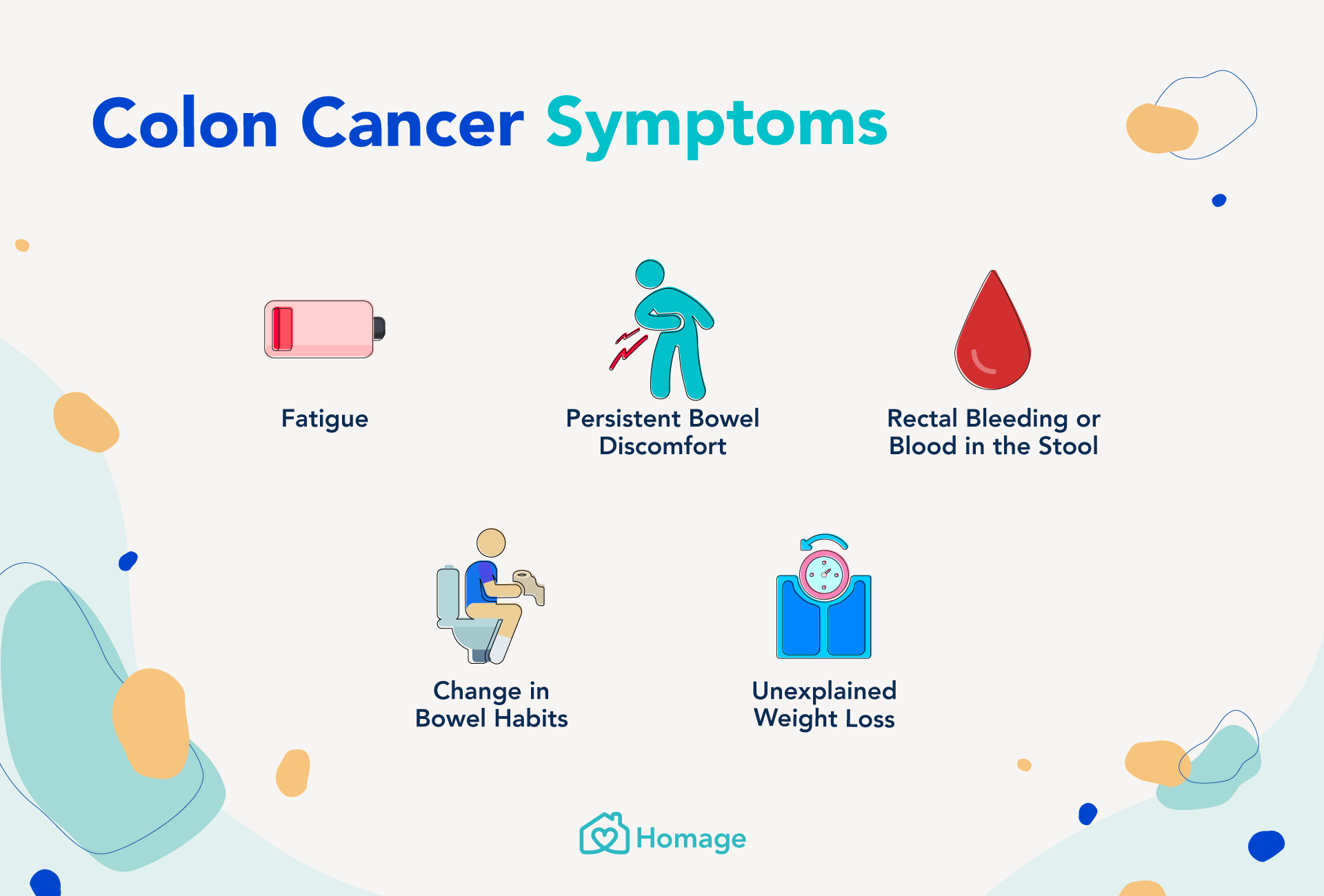
Common Symptoms of Pritchard Colon
Recognizing the symptoms of Pritchard Colon is the first step toward seeking appropriate medical care. The most common symptom is chronic constipation, which is defined as having fewer than three bowel movements per week for an extended period. However, Pritchard Colon often presents with additional symptoms that can help differentiate it from other digestive disorders.
Key Symptoms
- Infrequent Bowel Movements: Individuals with Pritchard Colon may go days or even weeks without a bowel movement.
- Bloating and Abdominal Distension: The buildup of stool in the colon can cause the abdomen to feel swollen and uncomfortable.
- Abdominal Pain: Cramping or sharp pain in the abdomen is a common complaint among those with this condition.
- Straining During Bowel Movements: Even when bowel movements occur, they may require significant effort and cause discomfort.
- Incomplete Evacuation: Many individuals feel as though they have not fully emptied their bowels after a movement.
It is important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and may overlap with other gastrointestinal conditions. Therefore, a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis.
The Diagnosis Process
Diagnosing Pritchard Colon can be a complex process, as its symptoms often mimic those of other digestive disorders. Healthcare providers typically begin with a detailed medical history and physical examination to rule out other potential causes of chronic constipation.
Read also:Aaron Eckhart Wife Discovering The Life Love And Legacy
Diagnostic Tests
- Colonoscopy: This procedure allows doctors to examine the colon for structural abnormalities or signs of disease.
- Colonic Transit Study: A specialized test that measures how quickly stool moves through the colon.
- Anorectal Manometry: This test evaluates the function of the muscles and nerves in the rectum and anus.
- Imaging Studies: X-rays or CT scans may be used to visualize the colon and identify any blockages or abnormalities.
These diagnostic tools, combined with a comprehensive evaluation, help healthcare providers determine whether Pritchard Colon is the underlying cause of a patient's symptoms. Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Causes and Risk Factors
While the exact cause of Pritchard Colon remains unclear, several factors may contribute to its development. Understanding these factors can help individuals identify potential risk factors and take preventive measures.
Potential Causes
- Neurological Abnormalities: Dysfunction in the nerves that control colon contractions may play a role.
- Muscular Issues: Weak or uncoordinated colon muscles can impair the movement of stool.
- Genetic Predisposition: Some individuals may have a family history of chronic constipation or related conditions.
- Hormonal Imbalances: Hormonal changes, particularly in women, may affect digestive function.
Certain lifestyle factors, such as a low-fiber diet, inadequate hydration, and lack of physical activity, can also increase the risk of developing Pritchard Colon. Addressing these factors through lifestyle modifications may help alleviate symptoms and improve overall digestive health.
Treatment Options for Pritchard Colon
Treating Pritchard Colon often requires a multifaceted approach that combines medical interventions, lifestyle changes, and dietary adjustments. The goal of treatment is to alleviate symptoms, improve bowel function, and enhance the patient's quality of life.
Medical Treatments
- Medications: Laxatives, stool softeners, and prokinetic agents may be prescribed to stimulate bowel movements.
- Biofeedback Therapy: This non-invasive treatment helps retrain the muscles of the pelvic floor to improve bowel function.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical options such as colectomy may be considered to remove the affected portion of the colon.
It is important to work closely with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan based on the severity of symptoms and individual needs.
Lifestyle Changes to Manage Symptoms
In addition to medical treatments, making lifestyle changes can significantly improve symptoms of Pritchard Colon. These changes focus on promoting regular bowel movements and supporting overall digestive health.
Recommended Changes
- Increase Fiber Intake: Consuming a diet rich in fiber can help soften stool and promote regularity.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for maintaining proper digestive function.
- Exercise Regularly: Physical activity can stimulate bowel movements and improve overall health.
- Establish a Routine: Setting aside time each day for bowel movements can help train the body to establish regular habits.
Implementing these lifestyle changes can complement medical treatments and provide long-term relief from symptoms.
Dietary Recommendations
Diet plays a crucial role in managing Pritchard Colon. Certain foods can exacerbate symptoms, while others can help alleviate them. Understanding which foods to include and avoid is essential for maintaining digestive health.
Foods to Include
- Fruits and Vegetables: High-fiber options like apples, pears, and broccoli can promote regularity.
- Whole Grains: Foods like oats, quinoa, and brown rice are excellent sources of fiber.
- Probiotics: Yogurt and fermented foods can support a healthy gut microbiome.
Foods to Avoid
- Processed Foods: These often lack fiber and can contribute to constipation.
- Dairy Products: Some individuals may experience worsening symptoms with excessive dairy consumption.
- Red Meat: High-fat meats can slow digestion and exacerbate symptoms.
By making mindful dietary choices, individuals with Pritchard Colon can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Medical Interventions and Procedures
For individuals with severe cases of Pritchard Colon, medical interventions may be necessary to address the underlying issues and provide relief from symptoms.
Advanced Options
- Colonic Irrigation: This procedure involves flushing the colon with water to remove impacted stool.
- Bowel Training Programs: Structured programs that teach individuals how to establish regular bowel habits.
- Minimally Invasive Surgery: Procedures such as sacral nerve stimulation may be considered for certain patients.
These interventions are typically reserved for cases where conservative treatments have failed to provide adequate relief. Consulting with a specialist is essential for determining the most appropriate course of action.
The Emotional Impact of Pritchard Colon
Living with Pritchard Colon can take a toll on an individual's mental and emotional well-being. Chronic constipation and its associated symptoms can lead to feelings of frustration, embarrassment, and isolation.
It is important for individuals to seek support from healthcare providers, support groups, or mental health professionals to address the emotional challenges of this condition. Developing coping strategies and connecting with others who understand the experience can provide much-needed relief and encouragement.
Conclusion and Next Steps
Pritchard Colon is a complex and often misunderstood condition that requires careful management and a comprehensive treatment approach. By understanding the symptoms, causes, and diagnostic procedures, individuals can take proactive steps toward improving their digestive health.
If you suspect you may have Pritchard Colon, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan. Additionally, making lifestyle changes, adopting a fiber-rich diet, and seeking emotional support can significantly enhance your quality of life.
We encourage you to share this article with others who may benefit from the information and to leave a comment below with your thoughts or experiences. Together, we can raise awareness and provide support for those living with Pritchard Colon.