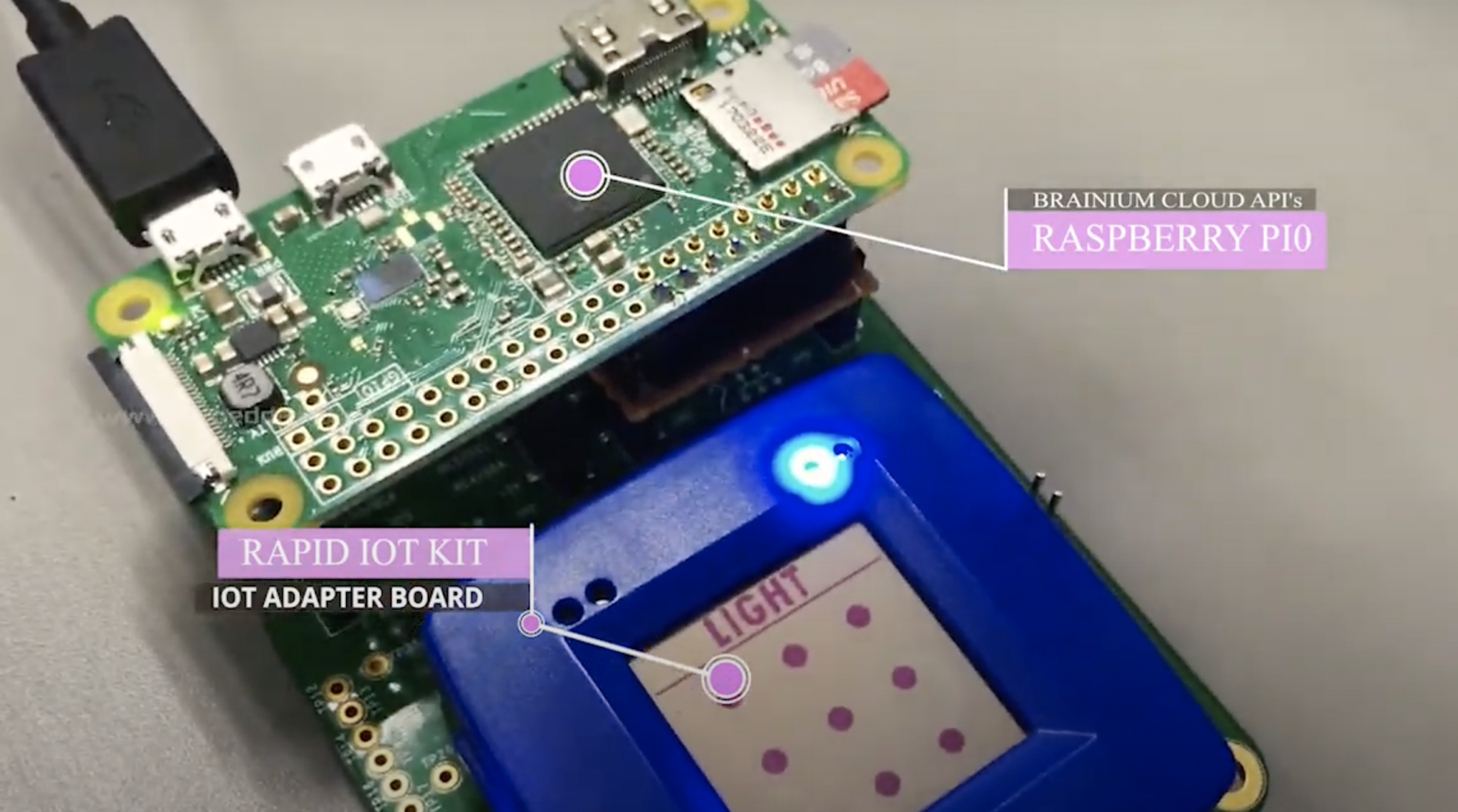
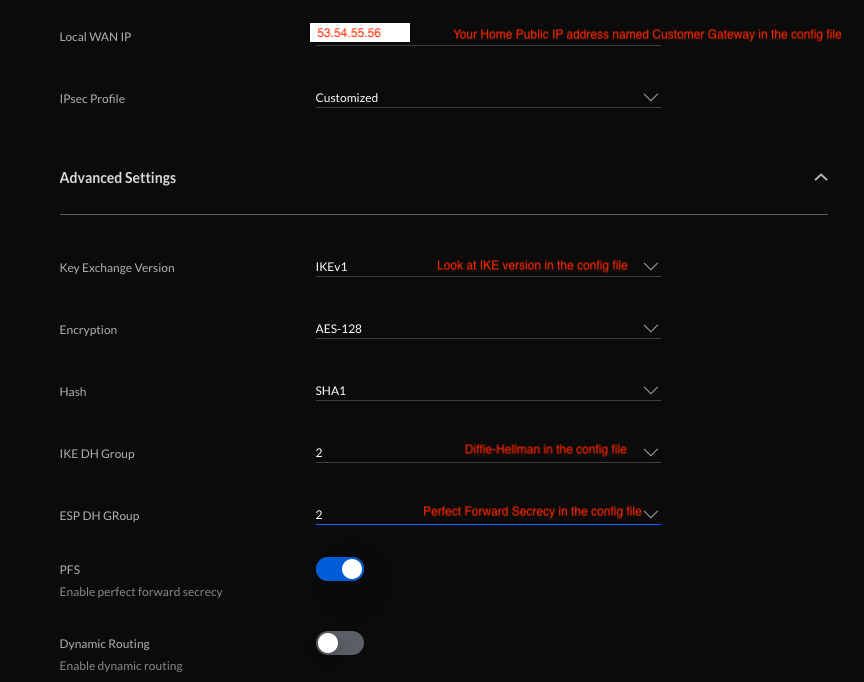
In today's interconnected world, the concept of remote IoT VPC network with Raspberry Pi has gained immense popularity among tech enthusiasts, hobbyists, and professionals alike. As IoT continues to evolve, the need for secure and efficient remote networking solutions becomes more critical than ever. By leveraging the power of Raspberry Pi, users can create a robust infrastructure to manage IoT devices remotely while maintaining security and scalability.
This article aims to provide an in-depth exploration of remote IoT VPC networks using Raspberry Pi. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, this guide will walk you through the fundamentals, advanced techniques, and best practices to help you set up and optimize your remote IoT network.
From understanding the basics of IoT and VPC networks to implementing real-world applications, we'll cover everything you need to know to take your IoT projects to the next level. Let's dive in and explore the possibilities of remote IoT VPC networks powered by Raspberry Pi.
Read also:Kannada New Movie Download A Comprehensive Guide For Film Enthusiasts
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to Remote IoT VPC Networks
- Raspberry Pi Overview
- Understanding IoT and VPC Basics
- Setting Up a Remote VPC Network
- Configuring Raspberry Pi for IoT
- Securing Your IoT Network
- Scaling Your Remote IoT Network
- Real-World Applications of Remote IoT VPC Networks
- Troubleshooting Common Issues
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to Remote IoT VPC Networks
Remote IoT VPC networks represent a cutting-edge solution for managing Internet of Things devices from anywhere in the world. A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) network provides a secure and isolated environment for IoT devices to communicate and exchange data. By integrating Raspberry Pi into this setup, users can create a cost-effective and scalable solution for their IoT projects.
With the growing demand for smart homes, industrial automation, and real-time monitoring systems, understanding how to build and manage remote IoT VPC networks is essential. This section will introduce the key concepts and benefits of using Raspberry Pi in IoT setups.
Raspberry Pi Overview
Raspberry Pi is a compact, affordable single-board computer that has revolutionized the way people approach computing and digital making. It is widely used in educational settings, home automation, and professional projects due to its versatility and ease of use.
Key Features of Raspberry Pi
- Compact and portable design
- Supports multiple operating systems, including Linux-based distributions
- Equipped with GPIO pins for hardware interfacing
- Low power consumption
These features make Raspberry Pi an ideal platform for developing remote IoT VPC networks.
Understanding IoT and VPC Basics
Before diving into the specifics of remote IoT VPC networks, it's important to understand the foundational concepts of IoT and VPC networks.
Read also:Movierulz Kannada 2025 Ndash Download Everything You Need To Know
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things refers to the network of physical devices, vehicles, home appliances, and other items embedded with sensors, software, and connectivity that enable them to collect and exchange data.
What is a VPC?
A Virtual Private Cloud is a private cloud hosted within a larger public cloud infrastructure. It provides a secure and isolated environment for running applications and managing resources.
By combining IoT and VPC, users can create a powerful platform for managing connected devices remotely.
Setting Up a Remote VPC Network
Setting up a remote VPC network involves several steps, from selecting the right cloud provider to configuring security settings. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
Step 1: Choose a Cloud Provider
Select a reputable cloud provider that supports VPC networks, such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Microsoft Azure. Each provider offers unique features and pricing plans, so it's important to choose one that aligns with your project requirements.
Step 2: Create a VPC Network
Follow the provider's documentation to create a VPC network. Ensure that you configure the necessary subnets, routing tables, and security groups to ensure secure communication between devices.
Step 3: Connect Raspberry Pi to the VPC
Once the VPC network is set up, connect your Raspberry Pi to it by configuring the necessary network settings. This may involve setting up static IP addresses and configuring SSH access for remote management.
Configuring Raspberry Pi for IoT
To fully leverage the capabilities of Raspberry Pi in an IoT setup, proper configuration is crucial. Below are some key steps to consider:
Install the Right Operating System
Choose an operating system that supports IoT applications, such as Raspbian or Ubuntu Server. These systems come with built-in tools and libraries that simplify IoT development.
Enable SSH Access
Secure Shell (SSH) is essential for remotely managing your Raspberry Pi. Ensure that SSH is enabled and configure firewall rules to restrict access to authorized users only.
Install Necessary Libraries
Install libraries and frameworks that support IoT development, such as MQTT for messaging and Python for scripting. These tools will help you build robust IoT applications.
Securing Your IoT Network
Security is a top priority when managing IoT devices remotely. Below are some best practices to secure your remote IoT VPC network:
Use Strong Authentication
Implement strong authentication mechanisms, such as two-factor authentication (2FA), to protect your network from unauthorized access.
Regularly Update Firmware
Keep all devices and software up to date with the latest security patches and updates. This helps mitigate vulnerabilities and ensures optimal performance.
Monitor Network Activity
Set up monitoring tools to track network activity and detect any suspicious behavior. This proactive approach can help prevent potential security breaches.
Scaling Your Remote IoT Network
As your IoT project grows, scalability becomes a critical consideration. Below are some strategies to scale your remote IoT VPC network:
Use Load Balancers
Implement load balancers to distribute traffic evenly across multiple devices, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
Optimize Resource Allocation
Monitor resource usage and adjust allocations as needed to accommodate increasing demands. This may involve adding more devices or upgrading existing hardware.
Automate Processes
Automate routine tasks, such as data collection and analysis, to reduce manual intervention and improve efficiency.
Real-World Applications of Remote IoT VPC Networks
Remote IoT VPC networks powered by Raspberry Pi have numerous applications across various industries. Below are some examples:
Smart Homes
Control lighting, temperature, and security systems remotely using IoT devices connected to a VPC network.
Industrial Automation
Monitor and manage industrial processes in real-time, improving efficiency and reducing downtime.
Agriculture
Implement precision farming techniques by collecting and analyzing data from IoT sensors deployed in fields.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
When working with remote IoT VPC networks, you may encounter various challenges. Below are some common issues and their solutions:
Network Connectivity Problems
Ensure that all devices are properly connected to the network and that firewall rules are correctly configured.
Device Malfunction
Check device logs for error messages and perform firmware updates if necessary.
Security Breaches
Investigate any unauthorized access attempts and reinforce security measures to prevent future incidents.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, remote IoT VPC networks powered by Raspberry Pi offer a powerful and flexible solution for managing IoT devices remotely. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can create a secure and scalable infrastructure for your IoT projects.
We encourage you to take action by experimenting with the techniques discussed in this article. Share your experiences and insights in the comments section below, and don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more valuable information.