In today's digital age, the internet has become an integral part of our daily lives. Whether you're browsing websites, shopping online, or accessing sensitive information, understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS is crucial. Both protocols play a vital role in how data is transmitted over the internet, but their differences significantly impact security and user trust. In this article, we'll explore the distinctions between HTTP and HTTPS, their implications, and why HTTPS is essential for modern web practices.
As websites continue to evolve, users demand more secure and reliable online experiences. The transition from HTTP to HTTPS has become a necessity for businesses and individuals alike. This shift not only enhances data protection but also improves user confidence when interacting with websites.
This article will delve into the technical aspects of HTTP and HTTPS, their differences, and the reasons behind the growing preference for HTTPS. By the end of this piece, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of why HTTPS matters and how it can benefit your online presence.
Read also:Movierulz 2025 Telugu The Ultimate Guide To Movie Streaming And Piracy Insights
Below is a table of contents to help you navigate through the article effortlessly:
Table of Contents
- Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
- History of HTTP
- What is HTTP?
- What is HTTPS?
- Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Why HTTPS is Important
- Security Features of HTTPS
- How to Switch to HTTPS
- Common Misconceptions About HTTP and HTTPS
- Conclusion and Call to Action
Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are communication protocols used to transfer data over the internet. While HTTP has been the standard for decades, HTTPS has emerged as the preferred choice for secure web browsing. Understanding the HTTP and HTTPS difference is essential for anyone managing a website or using the internet regularly.
Why Understanding HTTP and HTTPS Matters
The internet's rapid growth has led to an increase in cyber threats, making data security a top priority. HTTP lacks encryption, leaving sensitive information vulnerable to interception. On the other hand, HTTPS encrypts data, ensuring that communication between users and websites remains secure. This distinction is particularly important for websites handling personal or financial information.
History of HTTP
HTTP was first introduced in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. Over the years, it has undergone several revisions, with HTTP/1.1 being the most widely used version. However, as the internet evolved, the need for a more secure protocol became apparent, leading to the development of HTTPS.
Key Milestones in HTTP Development
- 1991: HTTP/0.9 introduced as the first version.
- 1996: HTTP/1.0 released, introducing features like persistent connections.
- 1997: HTTP/1.1 standardized, offering improved performance and reliability.
What is HTTP?
HTTP is a protocol used to transmit data over the internet. It operates on a client-server model, where a client (web browser) sends a request to a server, which then responds with the requested data. However, HTTP lacks encryption, making it susceptible to eavesdropping and data tampering.
How HTTP Works
When you visit a website using HTTP, your browser sends a request to the server hosting the site. The server processes the request and sends back the requested data. This process occurs in plain text, meaning anyone with access to the network can intercept and read the data being transmitted.
Read also:Movierulz 2021 Your Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Navigating The Streaming Phenomenon
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS is an extension of HTTP that adds a layer of security through encryption. It uses SSL/TLS (Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security) certificates to encrypt data, ensuring that communication between users and websites remains private and secure. This makes HTTPS the preferred choice for websites handling sensitive information.
How HTTPS Works
When you visit a website using HTTPS, your browser establishes a secure connection with the server using SSL/TLS encryption. This encryption ensures that any data exchanged between the browser and server cannot be intercepted or tampered with by third parties.
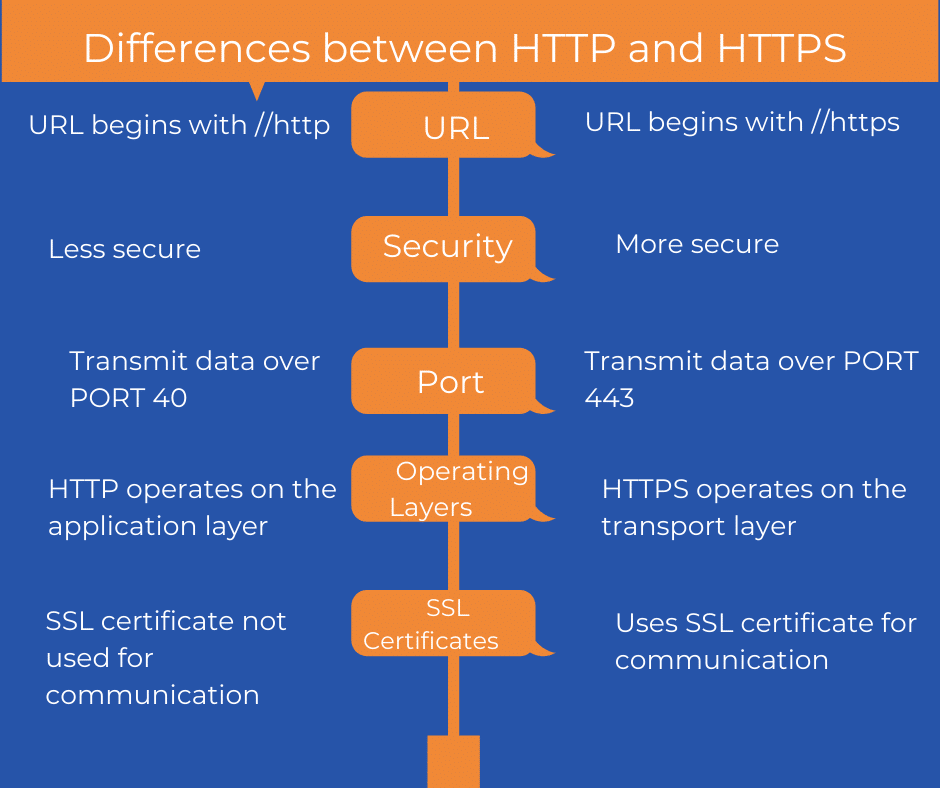
Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
The HTTP and HTTPS difference lies primarily in their approach to data security. Below are the key distinctions between the two protocols:
1. Security
- HTTP: Lacks encryption, making it vulnerable to attacks.
- HTTPS: Uses SSL/TLS encryption to protect data.
2. Performance
- HTTP: May experience slower load times due to unoptimized data transfer.
- HTTPS: Often faster due to modern encryption protocols like HTTP/2.
3. Trust
- HTTP: Users may perceive websites as less secure.
- HTTPS: Displays a padlock icon in the browser, enhancing user trust.
Why HTTPS is Important
In today's digital landscape, HTTPS is not just a preference but a necessity. It ensures data integrity, protects user privacy, and enhances website credibility. Additionally, search engines like Google prioritize HTTPS websites in search results, making it crucial for SEO performance.
Benefits of HTTPS
- Improved security for sensitive data.
- Enhanced user trust and confidence.
- Better search engine rankings.
- Compliance with industry standards and regulations.
Security Features of HTTPS
HTTPS employs several security features to protect data, including:
1. Encryption
HTTPS encrypts data using SSL/TLS certificates, ensuring that information remains private during transmission.
2. Authentication
HTTPS verifies the identity of websites, preventing phishing attacks and ensuring users interact with legitimate sites.
3. Data Integrity
HTTPS ensures that data cannot be altered during transmission, maintaining its accuracy and reliability.
How to Switch to HTTPS
Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS involves several steps, including obtaining an SSL/TLS certificate, updating website links, and configuring server settings. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you make the transition:
Step 1: Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate
Purchase an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). There are various types of certificates available, including Domain Validated (DV), Organization Validated (OV), and Extended Validation (EV) certificates.
Step 2: Install the Certificate
Install the SSL/TLS certificate on your web server. Most hosting providers offer tools to simplify this process.
Step 3: Update Internal Links
Replace all HTTP links within your website with HTTPS equivalents to avoid mixed content issues.
Step 4: Configure Server Settings
Set up your server to redirect HTTP traffic to HTTPS. This ensures that users always access your website securely.
Common Misconceptions About HTTP and HTTPS
Despite the widespread adoption of HTTPS, several misconceptions persist. Below are some common myths and the truths behind them:
1. HTTPS Slows Down Websites
Fact: Modern encryption protocols like HTTP/2 often make HTTPS faster than HTTP.
2. HTTPS is Only for E-commerce Sites
Fact: HTTPS benefits all websites by enhancing security and user trust.
3. HTTPS Eliminates All Cyber Threats
Fact: While HTTPS significantly improves security, it is not a cure-all solution. Additional security measures are still necessary.
Conclusion and Call to Action
In conclusion, understanding the HTTP and HTTPS difference is essential for anyone involved in web development or online activities. HTTPS offers superior security, improved user trust, and better search engine rankings, making it the preferred choice for modern websites. By switching to HTTPS, you can protect your users' data and enhance your website's credibility.
We encourage you to take action by securing your website with HTTPS. If you found this article helpful, please share it with others and explore more content on our website. Your feedback and support are invaluable to us!