Understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS is essential in today's digital world, where security and privacy are top priorities for both individuals and businesses. The internet has become an integral part of our lives, and knowing how data is transmitted online can help you make informed decisions about your online activities.
HTTP and HTTPS are protocols that govern how data is transferred across the web. While they might look similar, there are significant differences between the two, especially when it comes to security. As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll learn why HTTPS has become the standard for secure web communication.
In this article, we will explore the technical aspects of HTTP and HTTPS, their advantages and disadvantages, and why switching to HTTPS is crucial for websites. By the end of this guide, you'll have a clear understanding of what makes HTTPS more secure and how it impacts user trust and SEO.
Read also:Vegamovies Hollywood A Comprehensive Guide To The Intersection Of Veganism And The Film Industry
Table of Contents
- Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
- History of HTTP and HTTPS
- How HTTP Works
- How HTTPS Works
- Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Security Features of HTTPS
- Benefits of Using HTTPS
- Common Misconceptions About HTTPS
- Challenges of Migrating to HTTPS
- How to Switch to HTTPS
- Conclusion and Next Steps
Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are fundamental protocols that define how data is transmitted between your web browser and the server hosting the website you're visiting. While HTTP has been around since the early days of the internet, HTTPS emerged as a more secure alternative to address growing concerns about online privacy and data security.
The primary distinction between HTTP and HTTPS lies in the way data is transmitted. HTTP sends data in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception by malicious actors. On the other hand, HTTPS encrypts the data, ensuring that even if someone intercepts it, they won't be able to read or alter it without proper authorization.
As more businesses and individuals rely on the internet for transactions, communication, and information exchange, the importance of using secure protocols like HTTPS cannot be overstated. It not only protects sensitive information but also enhances user trust and improves search engine rankings.
History of HTTP and HTTPS
The development of HTTP and HTTPS reflects the evolution of the internet and the growing need for secure communication. HTTP was first introduced in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. It quickly became the standard protocol for transmitting web pages and other data over the internet.
However, as the internet grew and more sensitive information was being shared online, the need for a secure protocol became apparent. HTTPS was developed in the mid-1990s as an extension of HTTP, incorporating SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and later TLS (Transport Layer Security) to encrypt data during transmission.
Today, HTTPS is widely adopted by websites, especially those handling sensitive information such as online banking, e-commerce, and social media platforms. Its adoption has been further encouraged by search engines like Google, which prioritize HTTPS websites in their ranking algorithms.
Read also:Sone385 Unveiling The Rise Of A Phenomenal Music Sensation
How HTTP Works
HTTP operates on a request-response model, where a client (such as a web browser) sends a request to a server, and the server responds with the requested data. This process occurs in plain text, meaning that anyone who intercepts the communication can easily read the data being exchanged.
Here's a breakdown of how HTTP works:
- The client sends a request to the server using a specific URL.
- The server processes the request and sends back the requested data.
- The data is transmitted in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception by hackers.
While HTTP is simple and efficient, its lack of security makes it unsuitable for transmitting sensitive information. This is where HTTPS comes into play, offering a more secure alternative.
How HTTPS Works
HTTPS works similarly to HTTP but adds an extra layer of security through encryption. When a client connects to a server using HTTPS, the following steps occur:
- The client and server establish a secure connection using SSL/TLS.
- Data exchanged between the client and server is encrypted, ensuring that even if it's intercepted, it cannot be read without the decryption key.
- The server authenticates itself to the client using a digital certificate, verifying its identity.
This process ensures that data remains confidential, intact, and authentic during transmission, making HTTPS the preferred protocol for secure web communication.
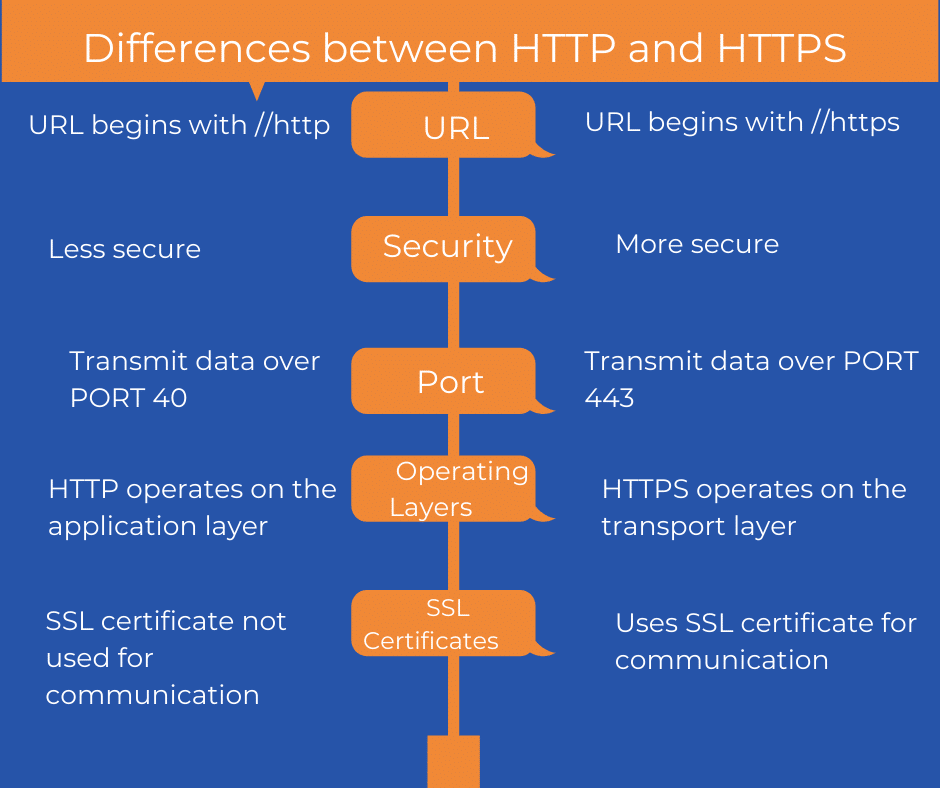
Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
While HTTP and HTTPS share similarities, there are several key differences that set them apart:
- Security: HTTPS encrypts data, while HTTP sends it in plain text.
- Port: HTTP uses port 80, whereas HTTPS uses port 443.
- Performance: HTTPS may introduce slight latency due to encryption, but modern technologies like HTTP/2 have minimized this impact.
- Trust: HTTPS websites display a padlock icon in the browser, indicating a secure connection.
These differences make HTTPS the preferred choice for websites that prioritize security and user trust.
Security Features of HTTPS
Encryption
Encryption is one of the core features of HTTPS. It ensures that data transmitted between the client and server is scrambled, making it unreadable to unauthorized parties. This is achieved through SSL/TLS protocols, which use complex algorithms to encrypt and decrypt data.
Data Integrity
HTTPS ensures that data remains unaltered during transmission. If someone attempts to modify the data, the encryption and hashing mechanisms will detect the changes, preventing unauthorized tampering.
Authentication
HTTPS verifies the identity of the server using digital certificates issued by trusted Certificate Authorities (CAs). This ensures that users are communicating with the legitimate website and not a fraudulent one.
Benefits of Using HTTPS
Switching to HTTPS offers numerous benefits, including:
- Improved security for sensitive data.
- Enhanced user trust, as indicated by the padlock icon in browsers.
- Better SEO rankings, as search engines prioritize HTTPS websites.
- Protection against data breaches and cyberattacks.
These advantages make HTTPS an essential component of modern web development and online security practices.
Common Misconceptions About HTTPS
Despite its widespread adoption, there are still misconceptions about HTTPS. Here are a few:
- HTTPS is only for e-commerce sites: While HTTPS is crucial for websites handling sensitive data, it's equally important for all websites to protect user privacy.
- HTTPS eliminates all security risks: While HTTPS significantly improves security, it doesn't protect against all types of cyberattacks, such as phishing or malware.
- HTTPS slows down websites: With advancements like HTTP/2, the performance impact of HTTPS is minimal.
Understanding these misconceptions can help website owners make informed decisions about implementing HTTPS.
Challenges of Migrating to HTTPS
Migrating to HTTPS can present some challenges, including:
- Obtaining and configuring SSL/TLS certificates.
- Updating internal and external links to reflect the new protocol.
- Ensuring proper redirection from HTTP to HTTPS.
However, these challenges can be overcome with proper planning and execution, and the benefits of HTTPS far outweigh the initial effort required.
How to Switch to HTTPS
Switching to HTTPS involves several steps:
- Choose a Certificate Authority (CA): Select a trusted CA to issue your SSL/TLS certificate.
- Install the Certificate: Follow the CA's instructions to install the certificate on your server.
- Update Internal Links: Ensure all internal links on your website use HTTPS.
- Set Up Redirects: Implement 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS to preserve SEO rankings.
By following these steps, you can successfully migrate your website to HTTPS and enjoy its numerous benefits.
Conclusion and Next Steps
In conclusion, understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS is crucial for ensuring secure and trustworthy online experiences. HTTPS offers enhanced security, user trust, and SEO advantages, making it the preferred protocol for modern websites.
To take the next step, consider migrating your website to HTTPS if you haven't already. Not only will it protect your users' data, but it will also improve your website's visibility and credibility. We encourage you to share this article with others and leave your thoughts in the comments below. For more insights into web security and optimization, explore our other articles on the site.