HTTP and HTTPS are two protocols used to transfer data over the internet. While both play a critical role in web communication, their differences can significantly impact security, trust, and user experience. In today's digital landscape, understanding these protocols is essential for website owners, developers, and users alike.
As the internet continues to evolve, so does the need for secure communication between websites and users. The distinction between HTTP and HTTPS has become increasingly important, particularly with the growing emphasis on online security and privacy. This article will explore the differences between the two protocols and highlight why HTTPS has become the preferred choice for modern websites.
By the end of this article, you'll have a comprehensive understanding of HTTP vs HTTPS, their advantages, disadvantages, and how they affect your online presence. Whether you're a business owner, developer, or casual internet user, this information will help you make informed decisions about web security.
Read also:5 Movierulz 2025 Download Your Ultimate Guide To Legal Streaming And Downloading Movies
Table of Contents
- Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
- The History of HTTP and HTTPS
- How HTTP and HTTPS Work
- Security Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Performance Impact of HTTP vs HTTPS
- SEO Benefits of HTTPS
- Building Trust with HTTPS
- Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS
- Common Issues with HTTPS Migration
- The Future of HTTP and HTTPS
Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
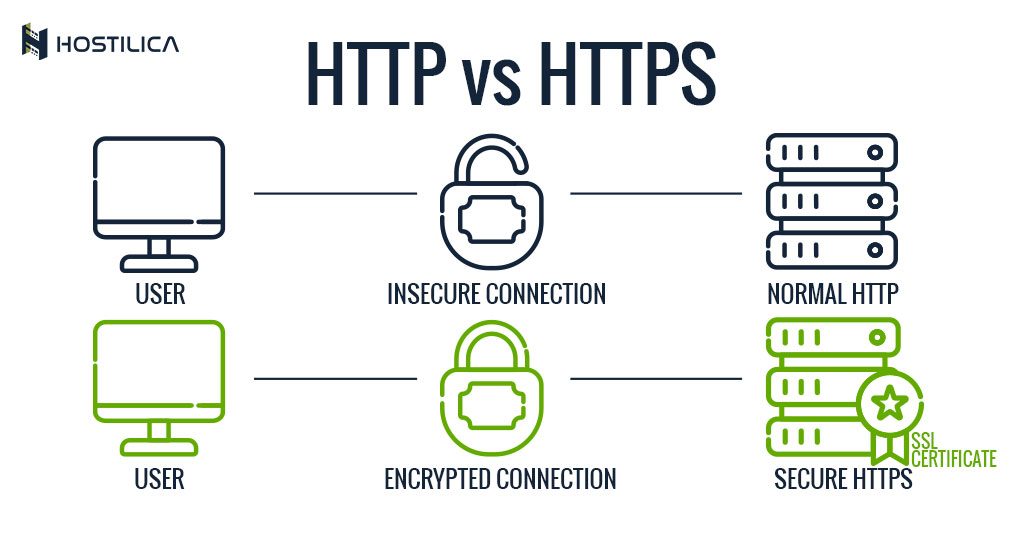
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are the foundation of data communication on the web. HTTP is the standard protocol used to transfer data between a web server and a browser, while HTTPS adds an extra layer of security through encryption.
One of the primary differences between HTTP and HTTPS lies in data security. HTTPS uses SSL/TLS certificates to encrypt data, ensuring that information transmitted between a user's browser and a website remains private and secure. This feature is especially important for websites that handle sensitive information, such as online banking, e-commerce, and healthcare platforms.
Why HTTPS Matters
HTTPS has become the industry standard for secure web communication. With increasing concerns about data breaches and cybercrime, websites that use HTTPS provide users with greater peace of mind. Below are some reasons why HTTPS is crucial:
- Protects sensitive information like passwords and credit card details
- Prevents unauthorized access to data during transmission
- Builds trust with users by displaying a secure connection in browsers
The History of HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP was first introduced in 1991 by Tim Berners-Lee, the inventor of the World Wide Web. Over the years, it has undergone several revisions, with HTTP/1.1 being the most widely used version. However, as the internet grew, so did the need for secure communication. This led to the development of HTTPS in the mid-1990s.
HTTPS uses SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) or its successor, TLS (Transport Layer Security), to encrypt data. Initially, HTTPS was primarily used for sensitive transactions, such as online banking and e-commerce. However, with the growing importance of web security, HTTPS has become the standard for all websites.
Key Milestones in the Evolution of HTTPS
- 1994: SSL 1.0 developed by Netscape
- 1996: SSL 3.0 released
- 1999: TLS 1.0 introduced as the successor to SSL
- 2018: Google Chrome begins marking HTTP sites as "Not Secure"
How HTTP and HTTPS Work
Understanding how HTTP and HTTPS function is essential to appreciate their differences. HTTP operates on a request-response model, where a client (browser) sends a request to a server, and the server responds with the requested data. This process is straightforward but lacks security.
Read also:Hdhub4u Bollywood Movies Your Ultimate Destination For Highquality Entertainment
HTTPS, on the other hand, incorporates encryption to secure data during transmission. When a user connects to an HTTPS site, the browser and server establish a secure connection through a handshake process. This involves exchanging cryptographic keys to ensure data integrity and confidentiality.
The SSL/TLS Handshake Process
The SSL/TLS handshake process involves several steps:
- Client sends a "hello" message to the server
- Server responds with its SSL/TLS certificate
- Client verifies the certificate and generates a pre-master secret
- Client and server use the pre-master secret to generate session keys
- Data is encrypted and decrypted using these session keys
Security Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
Security is one of the most significant distinctions between HTTP and HTTPS. HTTP transmits data in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception and tampering. This can lead to serious consequences, such as data breaches and identity theft.
HTTPS addresses these vulnerabilities by encrypting data using SSL/TLS certificates. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it cannot be read or altered without the decryption key. Additionally, HTTPS provides authentication, verifying that the website you're connecting to is legitimate.
Types of SSL/TLS Certificates
There are several types of SSL/TLS certificates, each offering different levels of security and validation:
- Domain Validated (DV): Basic level of validation, confirms ownership of the domain
- Organization Validated (OV): Requires additional verification of the organization's identity
- Extended Validation (EV): Most rigorous validation process, displays a green address bar in browsers
Performance Impact of HTTP vs HTTPS
A common misconception is that HTTPS slows down website performance. While encryption does introduce some overhead, advancements in technology have minimized this impact. In fact, modern browsers prioritize HTTPS connections, which can lead to faster load times.
Additionally, HTTP/2, the latest version of the HTTP protocol, is designed to work with HTTPS. It introduces features like multiplexing and header compression, further enhancing performance. As a result, websites using HTTPS can often outperform those using HTTP.
SEO Benefits of HTTPS
Google has long emphasized the importance of web security, and HTTPS plays a critical role in this regard. In 2014, Google announced that HTTPS would be a ranking signal in its search algorithm. Since then, websites using HTTPS have seen a competitive advantage in search engine results.
Beyond ranking benefits, HTTPS also improves user trust and engagement. Studies have shown that users are more likely to stay on a website and make purchases if they perceive it as secure. This can lead to increased traffic, conversions, and revenue.
Building Trust with HTTPS
Trust is a crucial factor in online interactions. Users are more likely to engage with a website if they feel their data is safe. HTTPS helps build trust by displaying a padlock icon in the browser's address bar, indicating a secure connection. For websites with EV certificates, this trust is further reinforced by displaying the organization's name in green.
Businesses that prioritize web security through HTTPS can differentiate themselves from competitors and foster stronger relationships with their customers. This trust can translate into increased brand loyalty and customer retention.
Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS
Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS is a straightforward process, but it requires careful planning and execution. Below are the key steps involved:
- Choose an SSL/TLS certificate provider and purchase the appropriate certificate
- Install the certificate on your web server
- Update internal links, scripts, and resources to use HTTPS
- Set up 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS
- Test your website to ensure all pages load securely
- Notify search engines about the migration through tools like Google Search Console
Best Practices for HTTPS Migration
To ensure a smooth transition, consider the following best practices:
- Use a trusted certificate authority
- Enable HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) to enforce HTTPS
- Monitor website performance and address any issues promptly
- Communicate the migration to users and stakeholders
Common Issues with HTTPS Migration
While migrating to HTTPS offers numerous benefits, it can also present challenges. Below are some common issues and how to address them:
- Mixed Content: Ensure all resources on your website use HTTPS to avoid mixed content errors.
- SSL Certificate Errors: Verify that your certificate is properly installed and configured.
- Performance Issues: Optimize your website to minimize the impact of encryption overhead.
- SEO Impact: Monitor search engine rankings and address any drops in traffic.
The Future of HTTP and HTTPS
As the internet continues to evolve, the importance of web security will only increase. HTTPS is likely to remain the standard for secure communication, with ongoing advancements in encryption and authentication technologies. In addition, initiatives like Let's Encrypt have made SSL/TLS certificates more accessible, encouraging widespread adoption.
Looking ahead, the focus will be on improving performance, enhancing user privacy, and addressing emerging threats. As a result, staying informed about the latest developments in web security is crucial for maintaining a safe and trustworthy online presence.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the differences between HTTP and HTTPS extend beyond technical specifications. HTTPS offers superior security, improved performance, and enhanced trust, making it the preferred choice for modern websites. By understanding the benefits of HTTPS and implementing it effectively, you can protect your users, improve your search engine rankings, and build a stronger online presence.
We encourage you to take action by migrating your website to HTTPS if you haven't already. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to explore other articles on our site for more insights into web security and optimization.