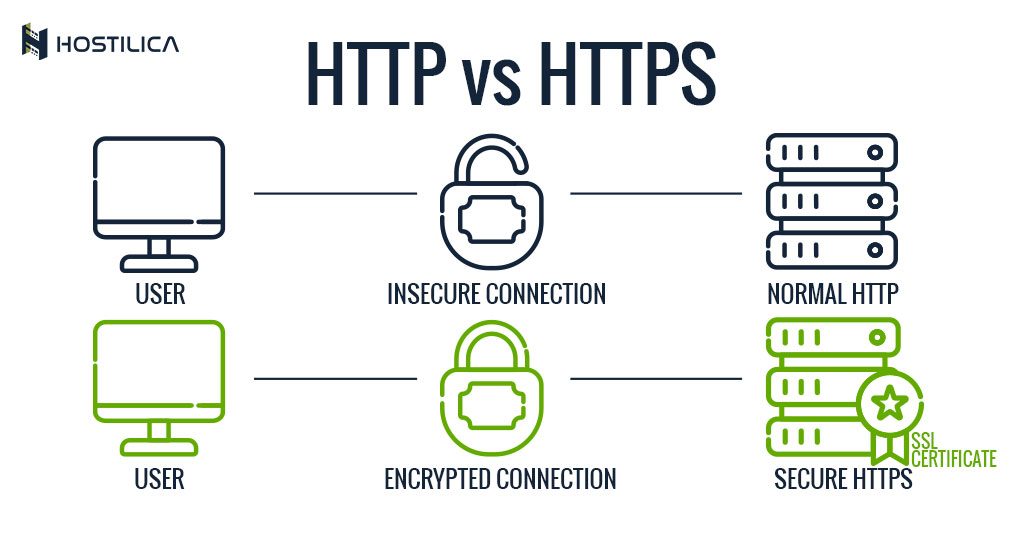
In today's digital age, understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS is crucial for both website owners and internet users. The distinction goes beyond technical jargon and has significant implications for security, trust, and user experience. As more websites transition to HTTPS, it's essential to comprehend why this shift is happening and what it means for your online presence.
With cyber threats becoming increasingly sophisticated, ensuring secure data transmission has never been more important. HTTP and HTTPS represent two different protocols that govern how information is exchanged between web servers and browsers. This article will delve into the core differences between these protocols, their impact on website performance, and why HTTPS has become the industry standard.
Whether you're a business owner looking to improve website security or a casual internet user wanting to stay safe online, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your online activities. Let's explore the world of HTTP and HTTPS and understand why the latter is indispensable in today's internet landscape.
Read also:5 Movierulz 2025 Download Your Ultimate Guide To Legal Streaming And Downloading Movies
Table of Contents:
- Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
- History of HTTP and HTTPS
- Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
- Benefits of Using HTTPS
- Security Features of HTTPS
- Impact on SEO and Web Performance
- Common Misconceptions About HTTPS
- Migration Process to HTTPS
- Costs Associated with HTTPS
- Future of Web Security
Introduction to HTTP and HTTPS
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) and HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) are fundamental protocols that govern how data is transmitted across the internet. HTTP was introduced in the early days of the web and served as the backbone of data communication. However, as the internet evolved, so did the need for enhanced security measures, leading to the development of HTTPS.
What is HTTP?
HTTP is a protocol used for transmitting information between web servers and clients. It operates on a request-response model, where a client (usually a web browser) sends a request to a server, and the server responds with the requested data. While HTTP is efficient and widely used, it lacks built-in security features, making it vulnerable to data interception and tampering.
What is HTTPS?
HTTPS is an extension of HTTP that incorporates encryption to secure data transmission. By utilizing SSL/TLS certificates, HTTPS ensures that the information exchanged between a web server and a browser remains private and tamper-proof. This added layer of security has made HTTPS the preferred protocol for websites handling sensitive data, such as online banking and e-commerce platforms.
Read also:Tamilblasters Forum The Ultimate Guide To Understanding And Navigating
History of HTTP and HTTPS
The journey of HTTP began in the late 1980s when Tim Berners-Lee developed the World Wide Web. HTTP version 0.9 was introduced in 1991, followed by HTTP/1.0 in 1996 and HTTP/1.1 in 1997. These iterations focused on improving efficiency and scalability but did not address security concerns.
The Emergence of HTTPS
HTTPS was first introduced in the mid-1990s as a solution to the growing need for secure data transmission. It utilizes SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) and later TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols to encrypt data. Over the years, HTTPS has become the standard for secure communication on the web, driven by increasing awareness of cyber threats and the need for user trust.
Key Differences Between HTTP and HTTPS
While HTTP and HTTPS share similarities, their fundamental differences lie in how they handle data transmission. Below are the primary distinctions between the two:
- Encryption: HTTPS encrypts data using SSL/TLS certificates, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure during transmission. HTTP, on the other hand, transmits data in plain text, making it vulnerable to interception.
- Port Usage: HTTP operates on port 80, while HTTPS uses port 443 for secure communication.
- Performance: HTTPS may introduce slight latency due to the encryption process, but advancements in technology have minimized this impact.
- Trust Indicators: Websites using HTTPS display a padlock icon in the browser address bar, signaling to users that the site is secure.
Benefits of Using HTTPS
Adopting HTTPS offers numerous advantages for both website owners and users. These benefits extend beyond security and impact various aspects of online presence. Some of the key advantages include:
Enhanced Security
HTTPS ensures that data transmitted between a website and its users remains private and protected from unauthorized access. This is particularly important for websites handling sensitive information, such as login credentials, financial data, and personal information.
Improved SEO Rankings
Google has publicly stated that HTTPS is a ranking factor in its search algorithm. Websites using HTTPS are more likely to appear higher in search results, giving them a competitive edge over non-secure sites.
Increased User Trust
The presence of a padlock icon in the browser address bar reassures users that their interactions with the website are secure, fostering trust and encouraging longer engagement.
Security Features of HTTPS
HTTPS incorporates several security features that make it a robust solution for protecting online data. These features include:
- Encryption: Data is encrypted using SSL/TLS protocols, preventing unauthorized access during transmission.
- Authentication: HTTPS verifies the identity of websites using digital certificates, ensuring users are connecting to legitimate sites.
- Data Integrity: HTTPS ensures that data remains unaltered during transmission, preventing tampering by malicious actors.
Impact on SEO and Web Performance
The transition to HTTPS has a significant impact on both search engine optimization (SEO) and web performance. While the initial migration may cause temporary performance issues, the long-term benefits outweigh the challenges. Below are some key points to consider:
SEO Benefits
Google prioritizes secure websites in its search rankings, giving HTTPS sites a boost in visibility. Additionally, users are more likely to engage with secure sites, leading to improved metrics such as bounce rate and session duration.
Web Performance Considerations
Although HTTPS introduces some latency due to encryption, modern advancements such as HTTP/2 and TLS 1.3 have significantly reduced this impact. In fact, HTTPS can enhance performance by enabling features like server push and multiplexing.
Common Misconceptions About HTTPS
Despite its widespread adoption, there are several misconceptions about HTTPS that need clarification. Addressing these myths can help businesses make informed decisions about implementing secure protocols. Some common misconceptions include:
- HTTPS is Only for E-commerce Sites: While HTTPS is essential for websites handling financial transactions, it benefits all sites by enhancing security and user trust.
- HTTPS Slows Down Websites: Advances in technology have minimized the performance impact of HTTPS, making it a viable option for all types of websites.
- HTTPS Eliminates All Security Risks: While HTTPS provides robust security features, it is not a panacea for all online threats. Websites must adopt a comprehensive security strategy to ensure complete protection.
Migration Process to HTTPS
Migrating from HTTP to HTTPS requires careful planning and execution to ensure a seamless transition. Below are the key steps involved in the migration process:
1. Obtain an SSL/TLS Certificate
Purchase an SSL/TLS certificate from a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). There are various types of certificates available, including Domain Validated (DV), Organization Validated (OV), and Extended Validation (EV). Choose the one that best suits your website's needs.
2. Update Internal Links
Ensure that all internal links, images, and resources are updated to use HTTPS. This prevents mixed content issues, where some elements on a page remain unsecured.
3. Redirect HTTP to HTTPS
Set up 301 redirects from HTTP to HTTPS to maintain SEO rankings and ensure users are directed to the secure version of your site.
Costs Associated with HTTPS
Implementing HTTPS involves certain costs, but these expenses are often outweighed by the benefits. The primary costs include:
- SSL/TLS Certificate Fees: Prices vary depending on the type of certificate and the issuing authority. Free certificates are also available through services like Let's Encrypt.
- Server Configuration: Configuring your server to support HTTPS may require additional resources and expertise.
- Ongoing Maintenance: Renewing certificates and monitoring security protocols are ongoing expenses associated with maintaining a secure website.
Future of Web Security
As technology continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of web security. The increasing adoption of HTTPS is just one step in the ongoing battle against cyber threats. Emerging technologies such as quantum encryption and blockchain hold promise for even more secure communication in the future.
Trends to Watch
Keep an eye on developments in areas such as zero-trust architecture, AI-driven threat detection, and advancements in encryption standards. These innovations will shape the future of web security and influence how we approach online safety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the difference between HTTP and HTTPS is essential for anyone involved in the digital world. HTTPS offers significant advantages in terms of security, SEO, and user trust, making it the preferred protocol for modern websites. By addressing common misconceptions and following best practices for migration, businesses can ensure a secure and successful online presence.
We encourage you to take action by securing your website with HTTPS. Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below, and don't forget to explore our other articles for more insights into web security and digital trends. Together, we can create a safer and more trustworthy internet for everyone.